DG Notes on 20170904 Event: Difference between revisions
| Line 673: | Line 673: | ||
return | return | ||
end | end | ||
== Less Aggressive Restoring Beam == | |||
I was not happy with the restoring beam I used when making the full suite of maps, which was the one Bin used for the 2017-Sep-10 event. Since I did like the images shown in the figures above, I have adjusted the parameters to be: | |||
sbeam = 40 | |||
bm=max(sbeam*cfreqs[1]/cfreq,10.) | |||
In addition, I thought the clean box was a bit off, and maybe too large, so I changed that to: | |||
mask='circle [ [ 123pix ,118pix] , 45pix ]', | |||
I hope this will result in somewhat better images, and maybe fewer spurious sources in some maps. | |||
Latest revision as of 20:46, 17 November 2018
Purpose
There are various scripts for doing the imaging and self calibration, but they require explanation on how to use them. This page is meant to provide step-by-step explanation on analyzing one event, the M5.5 flare that occurred on 2017-Sep-04. I earlier did an initial study of this event, but in a hurried fashion in order to use the results for a proposal (which was successful, by the way!). I would like to do a more careful job with the initial calibration and analysis, and then continue with a second round of self calibration.
Initial Preparation
The data begin as raw data in Miriad format, recorded to disk by the pipeline system, in the form of IDB files. These files each contain 10-min of data, with several such files together representing a scan. The easiest way to identify the time period of interest is to examine the overview spectral plots on the RHESSI Browser and check "EOVSA Radio Data" on the upper left. Use the time you identified to find the corresponding IDB file(s) under /data1/eovsa/fits/IDB/yyyymmdd/ (also accessible from the EOVSA web site. The scan containing this flare is a quite long one, starting 18:53:33 UT and continuing to 21:30:00 UT or so.
To know the exact time of interest takes some iteration, especially for such a long flare with several peaks and smaller events. After some checking, I settled on the three 10-min files starting at 20:23:33, 20:33:33, and 20:43:33 UT. Undoubtedly an additional one or two 10-min intervals after the end time of 20:53:33 would be useful for following the decay of the event, but in the interests of time analysis of these will be postponed.
Importing EOVSA Data
Once the desired timerange is known, the next step is to convert the raw IDB files to calibrated CASA ms files. The script below does this from within CASA, and must be run on pipeline, which has access to the raw data and the SQL database. This script may require 30 minutes or more to run.
from suncasa.tasks import task_calibeovsa as calibeovsa
from suncasa.tasks import task_importeovsa as timporteovsa
import dump_tsys as dt
from util import Time
import numpy as np
import os
# import copy
get_tp = True
workpath = '/data1/dgary/solar/20170904_Mflare/'
if not os.path.exists(workpath):
os.makedirs(workpath)
os.chdir(workpath)
# This time range will read files IDB20170904202333, IDB20170904203333, IDB20170904204333, and IDB20170904205333
trange = Time(['2017-09-04 20:20:00', '2017-09-04 21:00:00'])
info = dt.rd_fdb(Time('2017-09-04'))
sidx = np.where(
np.logical_and(info['SOURCEID'] == 'Sun', info['PROJECTID'] == 'NormalObserving') & np.logical_and(
info['ST_TS'].astype(np.float) >= trange[0].lv,
info['ST_TS'].astype(np.float) <= trange[1].lv))
filelist = info['FILE'][sidx]
outpath = 'msdata/'
if not os.path.exists(outpath):
os.makedirs(outpath)
inpath = '/data1/eovsa/fits/IDB/{}/'.format(trange[0].datetime.strftime("%Y%m%d"))
ncpu = 1
#
#
timporteovsa.importeovsa(idbfiles=[inpath + ll for ll in filelist], ncpu=ncpu, timebin="0s", width=1, visprefix=outpath,
nocreatms=False,
doconcat=False, modelms="", doscaling=False, keep_nsclms=False, udb_corr=True)
msfiles = [outpath + ll + '.ms' for ll in filelist]
# invis=copy.copy(msfiles)
concatvis = os.path.basename(msfiles[0])[:11] + '_2023-2103.ms'
vis = calibeovsa.calibeovsa(msfiles, caltype=['refpha', 'phacal'], interp='nearest', doflag=True, flagant='13~15',
doimage=False, doconcat=True,
msoutdir='msdata', concatvis=concatvis, keep_orig_ms=True)
This will result in the four measurement sets, IDB20170904202333.ms, IDB20170904203333.ms, IDB20170904204333.ms, and IDB20170904205333.ms being created and written to the current directory, and then concatenated into a single ms with the name IDB20170904_2023-2103.ms.
At this stage, the calibrated, concatenated ms can be transferred to baozi for further processing. For example, the command
tar -czf IDB20170904_2023-2103.ms.tgz IDB20170904_2023-2103.ms
creates a compressed tar file that can be copied directly to baozi if the appropriate tunnel exists, or it can be staged in two steps. The file is 1 GB in size, so it could take some time to transfer. Actually, it only takes 5 minutes when I open a tunnel to pipeline on local port 8666, and then use
scp -P 8666 user@localhost:/data1/dgary/solar/20170904_Mflare/msdata/IDB20170904_2023-2103.ms.tgz .
in MobaXterm.
Selfcal on Baozi
Once the file is transferred to Baozi (I untarred the file into /srg/dgary/eovsa/solar/20170904_Mflare/msdata), the first thing that is needed is to set up the environment:
source /srg/.setenv_baozi
The strategy for the first stage of selfcal is to make a clean image for a short duration of the flare, when the source structure is relatively simple and the signal-to-noise ratio is high, then use that model to correct the antenna-based phases to bring the resulting map closer to the model. Three iterations of phase-only selfcal are done in each of two stages.
The initial setup involves declaring the working directory and ms names, and splitting out a single polarization (this one is 'XX'):
from suncasa.utils import helioimage2fits as hf
import os
import numpy as np
#task handles
dofullsun=0
doslfcal=1
dosbd=0
dofinalclean=0
workdir='/srg/dgary/eovsa/solar/20170904_Mflare/msdata/'
refms = workdir+'IDB20170904_2023-2103.ms'
slfcalms = workdir+'IDB20170904_2023-2103.ms.XX.peak'
slfcaledms = workdir+'slfcal/IDB20170904_2023_2103.ms.XX.peak.slfcaled'
if not os.path.exists(slfcalms):
split(vis=refms,outputvis=slfcalms,correlation='XX')
listobs(slfcalms,listfile=slfcalms+'.listobs')
clearcal(slfcalms)
delmod(slfcalms)
spws=[str(s) for s in range(1,31)]
antennas='0~12'
pol='XX'
calprefix=workdir+'slfcal/caltbs/slf_2023'
imgprefix=workdir+'slfcal/images/slf_2023'
To make the clean image in CASA, one must first declare a phase center in RA, Dec coordinates, and a clean box (mask) within which to apply the clean algorithm. One way to do this is to generate a full Sun image for a relatively wide timerange, bandwidth, and largish cell size during the event, and then measure the coordinates from the image. This is done with the following clean command:
if dofullsun:
trange='2017/09/04/20:33:33~2017/09/04/20:43:33'
img_init=imgprefix+'_init'
os.system('rm -rf '+img_init+'*')
clean(vis=slfcalms,
antenna='0~10,12',
imagename=img_init,
spw='1~15',
mode='mfs',
timerange=trange,
imagermode='csclean',
psfmode='clark',
imsize=[512,512],
cell=['5arcsec'],
niter=50,
gain=0.05,
stokes=pol,
restoringbeam=['15arcsec'],
interactive=False,
usescratch=True)
viewer(img_init+'.image')
The last line displays the image in the CASA image viewer, from which the coordinates can be read with the mouse. From this image, the coordinate center of the emission was measured to be 'J2000 10h53m57 06d56m47'. This will be used as the phase center of the subsequent maps used as the selfcal model.
First Stage
There is a trade-off in doing selfcal in various bands, so the first stage calculates the model in overlapping CASA band ranges 1~5, 4~10, 8~15, 10~20, and 15~30. The EOVSA band numbers are 4 greater than these. Although the model image is made using grouped bands, that model is applied separately to individual bands within each range, i.e. the 1~5 model is applied to bands 1~4, the 4~10 model is applied to 5~9, the 8~15 model is applied to 10~14, the 15~20 model is applied to 15~19, and the 15~30 model is applied to 20~30. A script was used as below, where the setting of trange (trange='20:45:00~20:45:10'), phase center (phasecenter='J2000 10h53m57 06d56m47') and the clean mask (mask='circle [[128pix, 128pix], 60pix]') are the main changes needed from case to case.
if doslfcal:
os.system('rm -rf '+calprefix+'*')
os.system('rm -rf '+imgprefix+'*')
trange='20:45:00~20:45:10'
tb.open(slfcalms+'/SPECTRAL_WINDOW')
reffreqs=tb.getcol('REF_FREQUENCY')
bdwds=tb.getcol('TOTAL_BANDWIDTH')
cfreqs=reffreqs+bdwds/2.
tb.close()
sbeam=40.
strtmp=[t.replace(':',) for t in trange.split('~')]
timestr='t'+strtmp[0]+'-'+strtmp[1]
refantenna='0'
nround=3
niters=[100,100,200]
robusts=[1.0,1.0,1.0]
doapplycal=[1,1,1]
uvranges=[,,]
slftbs=[]
for n in range(nround):
slfcal_tb_g= calprefix+'.G'+str(n)
for sp in spws:
cfreq=cfreqs[int(sp)]
bm=max(sbeam*cfreqs[1]/cfreq,10.)
slfcal_img = imgprefix+'.spw'+sp.zfill(2)+'.slfcal'+str(n)
if int(sp) < 5:
spwran='1~5'
if int(sp) >= 5 and int(sp) < 10:
spwran='4~10'
if int(sp) >= 10 and int(sp) < 15:
spwran='8~15'
if int(sp) >= 15 and int(sp) < 20:
spwran='10~20'
if int(sp) >= 20:
spwran='15~30'
print 'using spw {0:s} as model'.format(spwran)
try:
clean(vis=slfcalms,
antenna=antennas,
imagename=slfcal_img,
uvrange=uvranges[n],
#spw=sp,
spw=spwran,
mode='mfs',
timerange=trange,
imagermode='csclean',
psfmode='clark',
imsize=[256,256],
cell=['3arcsec'],
niter=niters[n],
gain=0.05,
stokes=pol,
weighting='briggs',
robust=robusts[n],
phasecenter='J2000 10h53m57 06d56m47',
#mask='box [ [ 75pix , 90pix] , [205pix, 165pix ] ]',
mask='circle [ [ 128pix ,128pix] , 60pix ]',
restoringbeam=[str(bm)+'arcsec'],
interactive=False,
usescratch=True)
except:
print 'error in cleaning spw: '+sp
print 'using nearby spws for initial model'
sp_e=int(sp)+2
sp_i=int(sp)-2
if sp_i < 0:
sp_i = 0
if sp_e > 30:
sp_e = 30
sp_=str(sp_i)+'~'+str(sp_e)
try:
tget(clean)
spw=sp_
clean()
except:
print 'still not successful. abort...'
break
print 'processing spw: '+sp
# gain solution, phase only
gaincal(vis=slfcalms, refant=refantenna,antenna=antennas,caltable=slfcal_tb_g,spw=sp, uvrange=,\
#gaintable=slftbs,selectdata=True,timerange=trange,solint='inf',gaintype='G',calmode='p',\
gaintable=[],selectdata=True,timerange=trange,solint='inf',gaintype='G',calmode='p',\
combine=,minblperant=2,minsnr=3,append=True)
if not os.path.exists(slfcal_tb_g):
print 'No solution found in spw: '+sp
if os.path.exists(slfcal_tb_g):
slftbs=[slfcal_tb_g]
plotcal(caltable=slfcal_tb_g,antenna=antennas,xaxis='antenna',yaxis='phase',\
subplot=421,plotrange=[0,12,-180,180],iteration='spw')
if doapplycal[n]:
clearcal(slfcalms)
delmod(slfcalms)
applycal(vis=slfcalms,gaintable=slftbs,spw=','.join(spws),selectdata=True,\
antenna=antennas,interp='nearest',flagbackup=False,applymode='calonly',calwt=False)
if n < nround-1:
prompt=raw_input('Continuing to selfcal? ["<cr>" to continue, "y" to split out new ms, "n" to quit]')
if prompt.lower() == 'n':
if os.path.exists(slfcaledms):
os.system('rm -rf '+slfcaledms)
split(slfcalms,slfcaledms,datacolumn='corrected')
print 'Final calibrated ms is {0:s}'.format(slfcaledms)
break
if prompt.lower() == 'y':
slfcalms_=slfcalms+str(n)
if os.path.exists(slfcalms_):
os.system('rm -rf '+slfcalms_)
split(slfcalms,slfcalms_,datacolumn='corrected')
slfcalms=slfcalms_
else:
if os.path.exists(slfcaledms):
os.system('rm -rf '+slfcaledms)
split(slfcalms,slfcaledms,datacolumn='corrected')
print 'Final calibrated ms is {0:s}'.format(slfcaledms)
When this stage is completed, one can view the different stage images to gauge the improvement.
Second Stage
The strategy in the second stage of selfcal is to adjust the clean boxes more individually in case of significant source changes with frequency, and also to create model images separately for each band. Again, three iterations of selfcal are done at this stage. First, the directory structure is set up:
from suncasa.utils import helioimage2fits as hf
import os
import numpy as np
import pickle
import pdb
from matplotlib import gridspec as gridspec
from sunpy import map as smap
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import time
#task handles
domasks=1 #generate clean masks for selfcal model
doslfcal=0 #perform selfcal on a spw-by-spw basis
doapply=0 #apply the selfcal tables
doclean_slfcaled=0 #do final clean on the selfcaled visibility data
workdir='/srg/dgary/eovsa/solar/20170904_Mflare/msdata/'
slfcaldir=workdir+'slfcal2/'
imagedir=slfcaldir+'images/'
maskdir=slfcaldir+'masks/'
imagedir_final=slfcaldir+'images_final/'
imagedir_slfcaled=slfcaldir+'images_slfcaled/'
caltbdir=slfcaldir+'caltbs/'
if not os.path.exists(imagedir):
os.makedirs(imagedir)
if not os.path.exists(maskdir):
os.makedirs(maskdir)
if not os.path.exists(imagedir_final):
os.makedirs(imagedir_final)
if not os.path.exists(imagedir_slfcaled):
os.makedirs(imagedir_slfcaled)
if not os.path.exists(caltbdir):
os.makedirs(caltbdir)
refms = workdir+'slfcal/IDB20170904_2023_2103.ms.XX.peak.slfcaled/'
refms_slfcal = slfcaldir + os.path.basename(refms) + '.slfcal2'
refms_slfcaled = slfcaldir + os.path.basename(refms) + '.slfcaled2'
if not os.path.exists(refms_slfcal):
split(vis=refms,outputvis=refms_slfcal,datacolumn='data',correlation='XX')
Next, the clean masks are set up, separately for the bands 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7~12, 13~20, and 21~30, and interactive cleaning is done, giving the opportunity to set clean boxes for each range. I used the same 10-s timerange here as I used for stage 1. The clean masks are saved in slfcaldir+'masks_a.p'. I find that selecting the clean boxes is quite tedious from off campus, due to the lag in mouse double-click.
# selected times for generating self-calibration solutions, use one timerange for now
tranges=['2017/09/04/20:45:00~2017/09/04/20:45:10']
spws=[str(s+1) for s in range(30)]
antennas='0~12'
npix=512
nround=3 #number of slfcal cycles
subms_a=[]
slfcalms_a=[]
slfcaledms_a=[]
for t,trange in enumerate(tranges):
subms_ = slfcaldir+'IDB20170904.ms.t{0:d}.slfcal'.format(t)
slfcalms_ = slfcaldir+'IDB20170904.ms.t{0:d}.XX.slfcal'.format(t)
slfcaledms_ = slfcaldir+'IDB20170904.ms.t{0:d}.XX.slfcaled'.format(t)
if not os.path.exists(slfcalms_):
split(vis=refms,outputvis=slfcalms_,datacolumn='data',timerange=trange,correlation='XX')
if not os.path.exists(subms_):
split(vis=refms,outputvis=subms_,datacolumn='data',timerange=trange,correlation=)
slfcalms_a.append(slfcalms_)
subms_a.append(subms_)
slfcaledms_a.append(slfcaledms_)
#define spw ranges for each mask
spwrans=['1','2','3','4','5','6','7~12','13~20','21~30']
#if use the same mask for all spws
#spwrans=['1~30']
if domasks:
masks_a=[]
for t,trange in enumerate(tranges):
slfcalms=slfcalms_a[t]
clearcal(slfcalms)
delmod(slfcalms)
antennas='0~12'
pol='I'
calprefix=caltbdir+'slf_t{0:d}'.format(t)
imgprefix=maskdir+'slf_t{0:d}'.format(t)
# step 1: set up the clean masks
img_init=imgprefix+'_init_ar_'
os.system('rm -rf '+img_init+'*')
mask=[]
imnames=[]
for spwran in spwrans:
imname=img_init+spwran.replace('~','-')
try:
clean(vis=slfcalms,
antenna='0~12',
imagename=imname,
spw=spwran,
mode='mfs',
timerange=trange,
imagermode='csclean',
psfmode='clark',
imsize=[npix],
cell=['2arcsec'],
niter=1000,
gain=0.05,
stokes='XX',
restoringbeam=['20arcsec'],
phasecenter='J2000 10h53m57 06d56m47',
weighting='briggs',
robust=1.0,
interactive=True,
pbcor=True,
usescratch=False)
imnames.append(imname+'.image')
mask.append(imname+'.mask')
clnjunks = ['.flux', '.model', '.psf', '.residual']
for clnjunk in clnjunks:
if os.path.exists(imname + clnjunk):
shutil.rmtree(imname + clnjunk)
except:
print('error in cleaning spw: '+spwran)
masks_a.append(mask)
pickle.dump(masks_a,open(slfcaldir+'masks_a.p','wb'))
After the masks are complete, the band-by-band selfcal is done, with one iteration of phase, and two iterations of amplitude selfcal. The important things to change are the phasecenter in the clean command, and the x and y range limits, in arcsec, for creating the eomap fits files.
if doslfcal:
if not os.path.exists(slfcaldir+'masks_a.p') or not ('masks_a' in vars()):
print 'masks do not exist. Please run dopartsun first!'
masks_a=[]
if os.path.exists(slfcaldir+'masks_a.p'):
masks_a=pickle.load(open(slfcaldir+'masks_a.p','rb'))
os.system('rm -rf '+imagedir+'*')
#first step: make a mock caltable for the entire database
slftbs_a=[]
for t,trange in enumerate(tranges):
print('Processing '+str(t+1)+' in '+str(len(tranges))+' times: '+trange)
slftbs=[]
slfcalms=slfcalms_a[t]
slfcaledms=slfcaledms_a[t]
subms=subms_a[t]
masks=masks_a[t]
#map masks to each spw
#count how many spws in each spw range used for masking
nspw=[]
for spwran in spwrans:
if len(spwran) == 1:
nspw.append(1)
else:
(bg,ed)=spwran.split('~')
nspw.append(int(ed)-int(bg)+1)
masks_=[]
for (mask,nsp) in zip(masks,nspw):
masks_+=[mask]*nsp
calprefix=caltbdir+'slf_t{0:d}'.format(t)
imgprefix=imagedir+'slf_t{0:d}'.format(t)
tb.open(slfcalms+'/SPECTRAL_WINDOW')
reffreqs=tb.getcol('REF_FREQUENCY')
bdwds=tb.getcol('TOTAL_BANDWIDTH')
cfreqs=reffreqs+bdwds/2.
tb.close()
sbeam=40.
strtmp=[m.replace(':',) for m in trange.split('~')]
timestr='t'+strtmp[0]+'-'+strtmp[1]
refantenna='0'
niters=[100,300,500]
robusts=[1.0,0.5,0.0]
doapplycal=[1,1,1]
calmodes=['p','a','a']
uvranges=[,,]
for n in range(nround):
slfcal_tb_g= calprefix+'.G'+str(n)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12,10))
gs = gridspec.GridSpec(6, 5)
for s,sp in enumerate(spws):
print 'processing spw: '+sp
cfreq=cfreqs[int(sp)]
bm=max(sbeam*cfreqs[1]/cfreq,10.)
slfcal_img = imgprefix+'.spw'+sp.zfill(2)+'.slfcal'+str(n)
spwran = sp
mask = masks_[s]
print 'using spw {0:s} as model'.format(spwran)
print 'using mask {0:s}'.format(mask)
try:
clean(vis=slfcalms,
antenna=antennas,
imagename=slfcal_img,
uvrange=uvranges[n],
#spw=sp,
spw=spwran,
mode='mfs',
timerange=trange,
imagermode='csclean',
psfmode='clark',
imsize=[npix],
cell=['2arcsec'],
niter=niters[n],
gain=0.05,
#stokes='I',
stokes='XX', #use pol XX image as the model
weighting='briggs',
robust=robusts[n],
phasecenter='J2000 10h53m57 06d56m47',
mask=mask,
restoringbeam=[str(bm)+'arcsec'],
pbcor=False,
interactive=False,
usescratch=True)
if os.path.exists(slfcal_img+'.image'):
fitsfile=slfcal_img+'.fits'
hf.imreg(vis=slfcalms,imagefile=slfcal_img+'.image',fitsfile=fitsfile,
timerange=trange,usephacenter=False,toTb=True,verbose=False,overwrite=True)
clnjunks = ['.mask','.flux', '.model', '.psf', '.residual', '.image']
for clnjunk in clnjunks:
if os.path.exists(slfcal_img + clnjunk):
shutil.rmtree(slfcal_img + clnjunk)
ax = fig.add_subplot(gs[s])
eomap=smap.Map(fitsfile)
eomap.data=eomap.data.reshape((npix,npix))
eomap.plot_settings['cmap'] = plt.get_cmap('jet')
eomap.plot()
eomap.draw_limb()
eomap.draw_grid()
ax.set_title(' ')
ax.set_xlim([100,400])
ax.set_ylim([-380,-80])
except:
print 'error in cleaning spw: '+sp
print 'using nearby spws for initial model'
sp_e=int(sp)+2
sp_i=int(sp)-2
if sp_i < 0:
sp_i = 0
if sp_e > 30:
sp_e = 30
sp_=str(sp_i)+'~'+str(sp_e)
try:
tget(clean)
spw=sp_
clean()
except:
print 'still not successful. abort...'
break
# copy model from xx to yy
#pdb.set_trace()
#mods.cpxx2yy(slfcalms)
gaincal(vis=slfcalms, refant=refantenna,antenna=antennas,caltable=slfcal_tb_g,spw=sp, uvrange=,\
gaintable=[],selectdata=True,timerange=trange,solint='inf',gaintype='G',calmode=calmodes[n],\
combine=,minblperant=4,minsnr=2,append=True)
if not os.path.exists(slfcal_tb_g):
#listcal(vis=slfcalms, caltable=slfcal_table)
print 'No solution found in spw: '+sp
figname=imagedir+'slf_t{0:d}_n{1:d}.png'.format(t,n)
plt.savefig(figname)
time.sleep(10)
plt.close()
if os.path.exists(slfcal_tb_g):
slftbs.append(slfcal_tb_g)
slftb=[slfcal_tb_g]
os.chdir(slfcaldir)
if calmodes[n] == 'p':
plotcal(caltable=slfcal_tb_g,antenna='1~12',xaxis='freq',yaxis='phase',\
subplot=431,plotrange=[-1,-1,-180,180],iteration='antenna',figfile=slfcal_tb_g+'.png',showgui=False)
if calmodes[n] == 'a':
plotcal(caltable=slfcal_tb_g,antenna='1~12',xaxis='freq',yaxis='amp',\
subplot=431,plotrange=[-1,-1,0,2.],iteration='antenna',figfile=slfcal_tb_g+'.png',showgui=False)
os.chdir(workdir)
if doapplycal[n]:
clearcal(slfcalms)
delmod(slfcalms)
applycal(vis=slfcalms,gaintable=slftb,spw=','.join(spws),selectdata=True,\
antenna=antennas,interp='nearest',flagbackup=False,applymode='calonly',calwt=False)
if n < nround-1:
prompt=raw_input('Continuing to selfcal? ["<cr>" to continue, "y" to split out new ms, "n" to quit] ')
#prompt='y'
if prompt.lower() == 'n':
if os.path.exists(slfcaledms):
os.system('rm -rf '+slfcaledms)
split(subms,slfcaledms,datacolumn='corrected')
print 'Final calibrated ms is {0:s}'.format(slfcaledms)
break
if prompt.lower() == 'y':
slfcalms_=slfcalms+str(n)
if os.path.exists(slfcalms_):
os.system('rm -rf '+slfcalms_)
split(slfcalms,slfcalms_,datacolumn='corrected')
slfcalms=slfcalms_
else:
if os.path.exists(slfcaledms):
os.system('rm -rf '+slfcaledms)
split(slfcalms,slfcaledms,datacolumn='corrected')
print 'Final calibrated ms is {0:s}'.format(slfcaledms)
slftbs_a.append(slftbs)
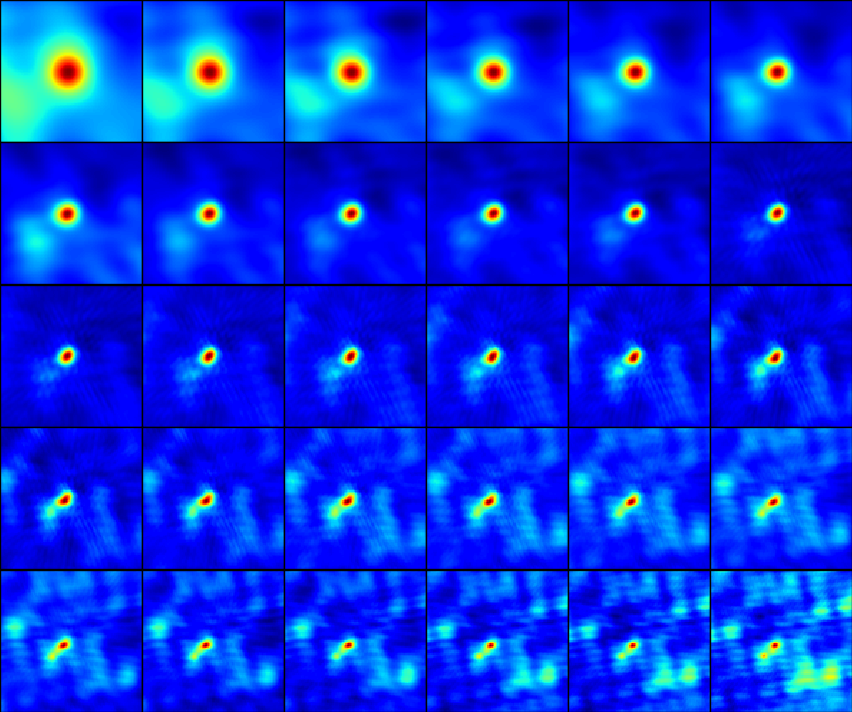
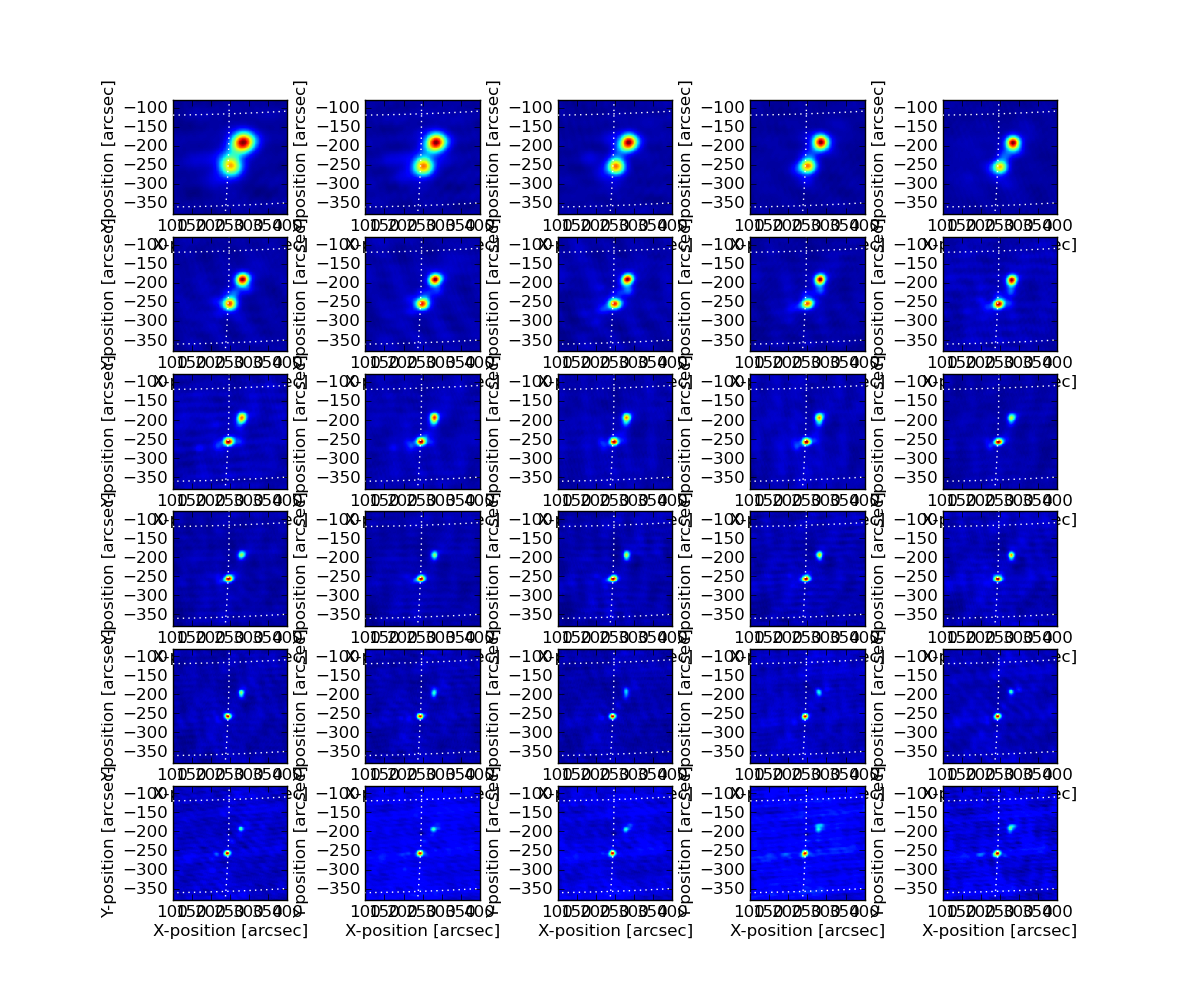
The result after running this procedure is a quite pleasing improvement, as shown in these two summary image matrices.
The final step is to apply the calibration tables to the original ms, to create the final selfcaled ms. The script section for this is
if doapply:
import glob
slftbs=[]
for n in range(nround):
tb=glob.glob(caltbdir+'slf_t*.G{0}'.format(n))
slftbs.append(tb[0])
clearcal(refms_slfcal)
applycal(vis=refms_slfcal,gaintable=slftbs,
spw=','.join(spws),selectdata=True,
antenna=antennas,interp='nearest',
flagbackup=False,applymode='calonly',
calwt=False)
if os.path.exists(refms_slfcaled):
os.system('rm -rf '+refms_slfcaled)
split(refms_slfcal,refms_slfcaled,datacolumn='corrected')
I made some images for other times from this selfcaled ms, and was at first a little disappointed, but I was using the clean masked created for the time 20:45:00 UT, which I now realize was too restricted in size. It nicely includes the double-footpoint source, but not the much weaker emission of the larger active region. The clean box needs to be enlarged to encompass this entire region, and in fact I can just go back to the large clean mask from stage 1, namely mask='circle [[128pix ,128pix], 60pix]'.
Making the full set of images
The imaging step is straightforward, although time consuming since there are so many images to make (18000 images). The script is:
from suncasa.utils import helioimage2fits as hf
import os
import numpy as np
from ptclean_cli import ptclean_cli as ptclean
########### Note do applycal cannot be run with
############doptclean in the same sesssion ######!
doptclean=1
workdir='/srg/dgary/eovsa/solar/20170904_Mflare/'
slfcaledms = workdir+'msdata/slfcal2/IDB20170904_2023_2103.ms.XX.peak.slfcaled.slfcaled2'
spws=[str(s+1) for s in range(30)]
antennas='0~10,12'
trange=
pol='XX'
if doptclean:
imgdir=workdir+'/allimages2step/'
spws=[str(s+1) for s in range(30)]
tb.open(slfcaledms+'/SPECTRAL_WINDOW')
reffreqs=tb.getcol('REF_FREQUENCY')
bdwds=tb.getcol('TOTAL_BANDWIDTH')
cfreqs=reffreqs+bdwds/2.
tb.close()
sbeam=30.
for s,sp in enumerate(spws):
cfreq=cfreqs[int(sp)]
bm=max(sbeam*cfreqs[0]/cfreq,6.)
imgprefix=imgdir+'s'+sp.zfill(2)+'_'
print 'cleaning spw {0:s} with beam size {1:.1f}"'.format(sp,bm)
try:
ptclean(vis=slfcaledms,
antenna=antennas,
imageprefix=imgprefix,
ncpu=20,
twidth=4,
doreg=True,
usephacenter=False,
toTb=True,
spw=sp,
mode='mfs',
timerange=trange,
imagermode='csclean',
psfmode='clark',
imsize=[256,256],
cell=['2arcsec'],
niter=1000,
gain=0.05,
stokes=pol,
weighting='briggs',
robust=0,
restoringbeam=[str(bm)+'arcsec'],
phasecenter='J2000 10h53m57 06d56m47',
#mask='box [ [ 75pix , 90pix] , [205pix, 165pix ] ]',
mask='circle [ [ 128pix ,128pix] , 50pix ]',
pbcor=True,
interactive=False,
usescratch=False)
except Exception as e:
print e
print 'cleaning spw '+sp+' unsuccessful. Proceed to next spw'
continue
After the imaging is completed, the flux integrated over the map must be compared with the total power spectrum to find scaling factors to adjust the spectra. A single scale factor is determined for the entire flare for each frequency. This should result in smoother spectra for fitting.
Converting fits files to IDL save file
After all of the images are completed, I run the following IDL procedure to convert them to a single IDL save file. This IDL procedure features the following:
- adding several keywords to the map structure,
- calculating the RMS deviations in one corner of the map,
- cutting out the central 300" x 300" portion of the map (151 x 151 pixels),
- calculating the signal to noise ratio (snr) in the map, where the signal is defined as the maximum in the "used" part of the map,
- putting the frequency, rms, and snr in each map structure,
- comparing the integrated flux density in the "used" part of the map with a total power spectrum ('eovsa_20170904_dynspec.sav') to obtain a scale factor to match the map flux with the total power spectrum,
- writing the scale factor into each map structure
Here is the complete procedure:
pro fits2sav2step
; Run in /srg/dgary/eovsa/solar/20170904_Mflare on baozi
restore,'eovsa_20170904_dynspec.sav',/ver
blist = fix((fghz - 2.86)*2)
t_tp = anytim(etime)
; Get file names in folder
cd,'allimages2step'
files = file_search('s01_*.fits',count=n)
; Get time list of sorted filenames for band 1 (600 times with no gaps)
tlist = strmid(files,13,6) ; format is 'HHMMSS'
; Read all files (bands + times)
files = file_search('*.fits',count=n)
; Get first map
fits2map,files[0],omap
rmsidx = where(shift(dist(256),128,128) gt 90)
rms = omap.data[rmsidx]
sdev = sqrt((moment(rms,/nan))[1])
sub_map,omap,map,xrange=[100,400],yrange=[-375,-75]
; Add various properties to this "template" map
add_prop,map,rms=sdev
add_prop,map,snr=max(map.data)/sdev
add_prop,map,scalefac=1.0
add_prop,map,rmsxran=[400.,500.]
add_prop,map,rmsyran=[-160.,-60.]
add_prop,map,dataunits='K'
add_prop,map,rmsunits='K'
add_prop,map,freq=2.92 + 0.5
add_prop,map,frequnit='GHz'
add_prop,map,stokes='XX'
map.id = 'EOVSA 0.00 GHz'
; Allocate memory for all maps (30 frequencies and 600 times)
eomaps = replicate(map,30,600)
k = 0
; Loop over maps
for i = 0, n-1 do begin
reads,strmid(files[i],1,2),k ; Read band id as integer k
fits2map,files[i],omap
sub_map,omap,map,xrange=[100,400],yrange=[-375,-75]
freq = 2.92 + k*0.5
mapflux = 2*1.38e-1*(freq*1e9)^2/(3e8)^2 * (2./206265.)^2 * total(map.data)
idx = where(tlist eq strmid(files[i],13,6),cnt)
if cnt eq 1 then begin
print,k,idx
eomaps[k-1,idx].data = map.data
eomaps[k-1,idx].time = map.time
eomaps[k-1,idx].l0 = map.l0
eomaps[k-1,idx].b0 = map.b0
eomaps[k-1,idx].rsun = map.rsun
eomaps[k-1,idx].id = 'EOVSA ' + string(freq,format='(F5.2)') + ' GHz'
eomaps[k-1,idx].freq = freq
rms = omap.data[rmsidx]
sdev = sqrt((moment(rms,/nan))[1])
eomaps[k-1,idx].snr = max(map.data)/sdev
; Get scale factor for this band and time
tidx = (where(anytim(map.time) lt t_tp))[0]
tpflux = mean(med[tidx,where(blist eq k)])
fac = tpflux/mapflux
; Write into map the scale factor needed to match TP
eomaps[k-1,idx].data = map.data
eomaps[k-1,idx].rms = sdev
eomaps[k-1,idx].scalefac = fac
endif
endfor
cd,'/srg/dgary/eovsa/solar/20170904_Mflare'
save,file='20170904_2step.sav',eomaps
return
end
Less Aggressive Restoring Beam
I was not happy with the restoring beam I used when making the full suite of maps, which was the one Bin used for the 2017-Sep-10 event. Since I did like the images shown in the figures above, I have adjusted the parameters to be:
sbeam = 40 bm=max(sbeam*cfreqs[1]/cfreq,10.)
In addition, I thought the clean box was a bit off, and maybe too large, so I changed that to:
mask='circle [ [ 123pix ,118pix] , 45pix ]',
I hope this will result in somewhat better images, and maybe fewer spurious sources in some maps.